Reference → OEV Network → Auction Cycle
Reference → OEV Network → Auction CycleAuction Cycle
The OEV Network uses an on-chain auction mechanism to facilitate the distribution of conditional oracle updates. The condition embedded in the oracle update is the value that the searcher is willing to pay to for the update to the beneficiary of the dAPI proxy.
To fully understand the auction mechanism let's break down the auction cycle using the following sequence diagram:
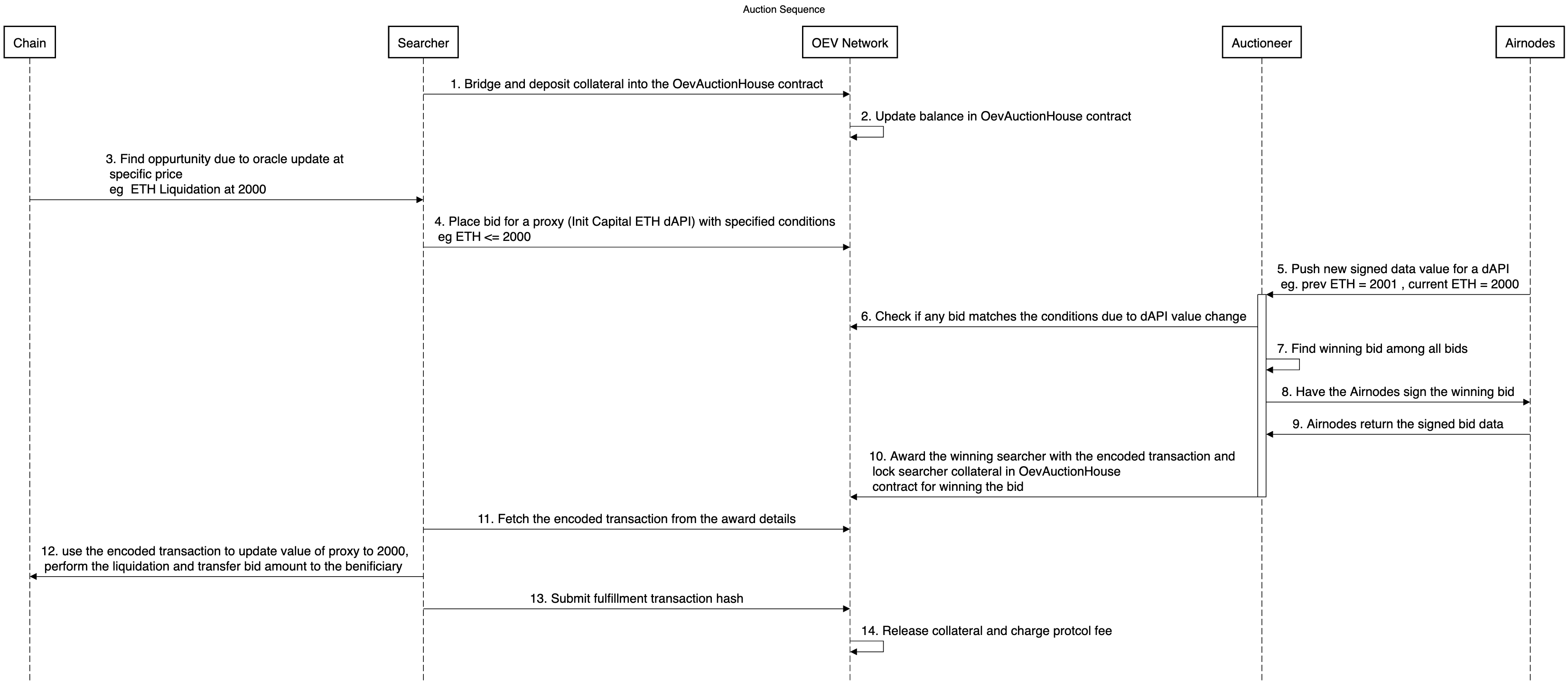
The auction cycle consists of the following steps:
- Bridging to the OEV Network
In order to interact with the OEV Network and participate in the auction the searcher needs to bridge their ETH to the OEV Network and deposit ETH into the OevAuctionHouse contract.
- Update searcher balance in OevAuctionHouse
Depositing ETH updates the searcher's balance in the OevAuctionHouse contract. The deposited ETH serves as Collateral which is needed to be able to win in the auction. The amount of Collateral needed is a percentage of the bid amount.
- Identify profitable oracle update
The searcher identifies conditions for an oracle update that would be valuable, for example a liquidation event if the price of ETH falls below 2000.
- Submitting a bid
The searcher would then submit a bid to the OevAuctionHouse contract with the specified conditions to receive the price update, i.e. price of ETH <= 2000. In order to submit a bid, the searcher doesn't need to have collateral deposited in the OevAuctionHouse contract. However for a bid to be eligible to win an auction, a collateral deposit in the OevAuctionHouse contract is required. The collateral doesn't get locked until the bid is awarded.
- Start of a new Auction Round
An auction rounds starts when the auctioneer receives a dAPI value update from Airnodes (eg: ETH/USD = 2000) or new blocks are produced on the OEV Network.
Auction Rounds
Off-chain Airnodes stream dAPI values to the auctioneer. Whenever there is a change in the dAPI value, the auctioneer would check if the new dAPI value satisfies the conditions of any of the bids on the OevAuctionHouse contract. If no bids are satisfied, the auctioneer waits for the next dAPI value change or new bids being placed. If a bid has just won an auction, the auctioneer waits for 60 seconds before starting the next auction round for that dAPI proxy.
In addition to fetching dAPI values, the auctioneer also fetches new blocks on the OEV Network periodically. The auctioneer checks if new bids have been placed and if any of the bids are satisfied by the current dAPI value. If no bids are satisfied, the auctioneer waits for the next block or dAPI value change. If a bid has just won an auction, the auctioneer waits for 60 seconds before starting the next auction round for that dAPI proxy.
- Check for bid conditions
The auctioneer checks the current dAPI value against bids received from the OevAuctionHouse contract to determine if any of the bid's conditions have been met.
- Finding the winning bid
If there are multiple bids that are satisfied, the auctioneer finds the winning bid by selecting the one with the highest bid amount. More details on how the auctioneer selects the winning bid can be found in the Understanding Auctioneer page.
- Sign the winning bid
The winning bid is sent to the Airnodes to obtain a signature allowing the searcher to update the dAPI value for the given proxy. These signatures are then processed by Auctioneer to prepare the update transaction calldata for searchers' convenience.
- Fetch the signatures for the awarded bid from the airnodes
The auctioneer fetches airnode signatures for the data feed update. These signatures are verified on-chain by the Api3ServerV1 contract to ensure that the update is valid and is triggered by the searcher who won the auction.
- Award the winning bid
The auctioneer publishes the winning bid along with the encoded calldata together with signatures to the OevAuctionHouse contract. The collateral of the winning bid is locked in the OevAuctionHouse contract in the same transaction that the winning bid is awarded.
- Fetch the awarded bid transaction
The searcher fetches the awarded bid transaction from the OEV Network. This transaction contains the encoded calldata. The searcher has 60 second window of exclusivity period to trigger the oracle update.
- Triggering the oracle update
The searcher can then use the encoded calldata to trigger the oracle update on the dAPI proxy and trigger the liquidation event atomically in a multicall transaction. The searcher can only do the price update if they transfer the bid amount to the beneficiary of the dAPI proxy.
- Submit fulfillment transaction hash to OevAuctionHouse
The searcher submits the fulfillment transaction hash to the OevAuctionHouse contract to confirm that the oracle update has been triggered. The searcher has a 24 hour window to submit the fulfillment transaction hash. In the event that the searcher does not submit the fulfillment transaction hash, the collateral of the winning bid is slashed.
- Release collateral and charge protocol fee
Once the fulfillment transaction hash is submitted, the collateral of the winning bid is released and the protocol fee is charged.